
Using CT, Korean researchers have been able to accurately locate and diagnose damage produced in the lungs of patients who have accidentally swallowed fuel while siphoning it from car tanks.

Using CT, Korean researchers have been able to accurately locate and diagnose damage produced in the lungs of patients who have accidentally swallowed fuel while siphoning it from car tanks.

OEM-software supplier ContextVision, its sister provider of end user products SharpView, and the Massachusetts General Hospital are investigating advanced 3D image filtering as a means to boost productivity and improve image quality for MRI, as well as cut dose in CT.

Medical imagers can now expect Medicare to routinely cover FDG-PET for initial staging of cervical cancer, thanks to a national coverage ruling announced Nov. 10.

A hospital run by Harrisburg, PA-based PinnacleHealth has become the first in the U.S. to install Toshiba America Medical Systems’ Aquilion Premium.

Imaging advocates, including the American College of Cardiology, cautioned against giving too much credence to a study in the New England Journal of Medicine concluding that adults are exposed to excessive doses of radiation from medical imaging procedures that are not supported by the clinical data.

A Boston University-led research team has come up with a breed of contrast agents that might open the door to the use of CT to noninvasively diagnose osteoarthritis. These agents visualize the distribution of glycosaminoglycans, the anionic sugars that account for the strength of joint cartilage.

Imaging experts are cautioning physicians not to rush to CT scanning for H1N1 flu patients, despite studies suggesting that chest CT is better than general radiography.

Developers of CT scanners have been trying to adapt their technology to breast imaging for decades. They have drawn a step closer, thanks to the efforts of researchers at the University of California, Davis. Their efforts may lead to the ability to not only visualize but treat breast cancer.

Partners Healthcare System in Boston has boosted CT contrast safety and saved money through a unique program that integrates contrast policies into the six-hospital system’s electronic medical records system, according to a new report.

Refurbished Aquilion CTs are now available from Toshiba America Medical Systems under a new program announced Nov. 10.

Medication errors may arise less often in a busy hospital radiology department than in other inpatient services, but they can cause more serious damage when they do happen. Radiologists at Boston-based Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center came to these conclusions after evaluating 27 months of high-tech medical imaging experience. They used their data to identify the causes of errors and devise strategies to address them.

Dose reduction will be among Siemens’ key messages at the RSNA meeting this year. Driving home this message will be IRIS (iterative reconstruction in image space), a proprietary algorithm that processes raw data acquired by CTs, according to André Hartung, Siemens vice president, CT Marketing and Sales.

With years of slice wars behind them, vendors will argue that image quality and dose reduction are this year’s dominant issues in CT. Most of their arguments will be rooted in past developments.

SNM's Clinical Trials Network has expanded to include relationships with European PET radiopharmaceutical manufacturing sites to support molecular and nuclear imaging facilities on the continent that are gearing up to perform scientific studies for the program.

At RSNA 2009 Bracco Diagnostics will highlight pre-programmed protocols integrated into its CT contrast injectors.

The American College of Radiology is predicting that imaging access will plunge and patient waiting times will soar from new Medicare Physician Fee Schedule rules that will cut Medicare payments for outpatient imaging by an estimated 16% next year.

CMS will increase the equipment utilization rate assumption used to determine the practice expense for all nontherapeutic medical equipment, including diagnostic imaging systems, from 50% to 90% under new Medicare fee schedule rules announced Friday. In a bit of good news for radiology, CMS said it remains on track to require that suppliers of advanced imaging services become accredited by 2012.

Impact on patient safety, hospital stay lead list of vendor priorities for scanner enhancements.
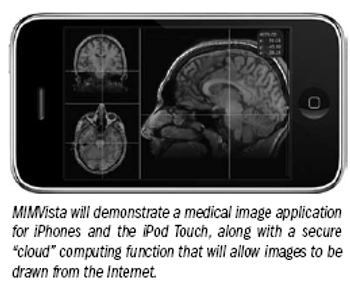
Specialties outside of radiology could benefit from unified databases and iPhone applications.

Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, the prestigious Los Angeles healthcare institution known as the hospital to the Hollywood stars, has been jolted by an FDA alert indicating that perfusion CT performed during an 18-month period exposed more than 200 stroke patients to eight times the normal dose of ionizing radiation for the procedures.

Swine flu patients are at risk of developing severe complications, such as pulmonary emboli, according to University of Michigan researchers. Most chest x-rays come back normal, so it’s especially important for radiologists to look closely for risks of blocked arteries in the lungs.

It should come as no surprise that the nuclear medicine community is struggling to keep up with the number of prescribed heart and bone exams. Technetium is typically used in the U.S. for more than 16 million nuclear medicine tests each year-but not this year. A survey by the SNM found that three quarters of nuclear medicine physicians are delaying patient tests, in many cases longer than a month. A shortage of medical-grade molybdenum-99 (Mo-99), the isotope critical to generating technetium, is the reason.

Teleradiology's aggressive move into day read business gives hospitaladministrators a 'nuclear option' against defiant hospital-based radiologists

Coronary artery calcium scoring has been tested at the University of Western Ontario to flag nuclear myocardial perfusion scans that missed the presence of three-vessel coronary artery disease, and to triage patients who need coronary CT angiography or cardiac catheterization.

Nuclear imagers are using alternatives to keep their practices alive until the National Research Universal Reactor at Chalk River, ON, resumes production of Mo-99