
Young male presents with foot pain after injury. What most likely represents the imaging finding?

Young male presents with foot pain after injury. What most likely represents the imaging finding?
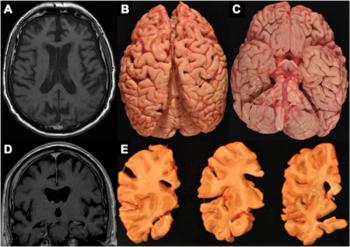
Emerging research suggests that frontotemporal atrophy on magnetic resonance imaging may be a key finding for chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).

Pertinent perspectives on emerging trends in radiology.

Why it behooves radiology recruiters to include compensation in job posts

What is the finding seen on this barium swallow?
Addition of late contrast enhancement (LCE) CT reportedly bolsters diagnostic rate for patients with acute chest pain who have negative findings on triple-rule-out (TRO) CT.
GE Healthcare unveils on-site detection upgrades and other advances with CT system as well as a new MRI device.
New research emphasizes roles of anterior collaterals and ischemic core growth rate in assessing patients with large vessel occlusion.

Technologies must be integrated with existing platforms and workflows, as well as demonstrate value.
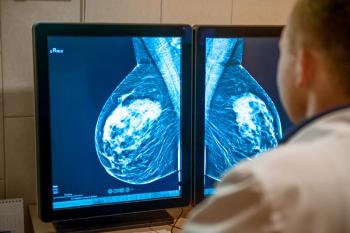
Warning systems designed to streamline interpretation of screening mammograms may not benefit interpreting radiologists or patients, a new study suggests.
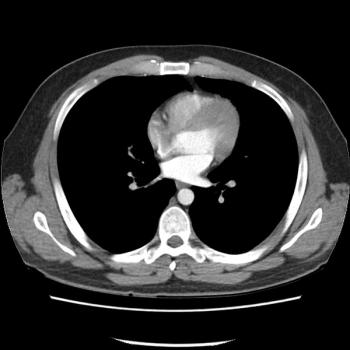
Study findings further highlight the central role of PET/CT in disease response after CAR-T cell therapy.
There isn't a person that hasn't been impacted by the pandemic, but what we can do is grow from the challenges we face and share what we've learned along the way.
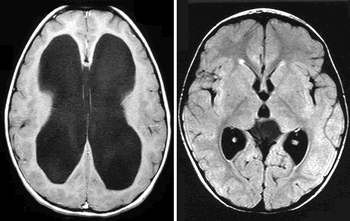
Early study results suggest that low-field MRI may offer a cost-effective, radiation-free alternative to monitor ventricular volume changes in patients with hydrocephalus.
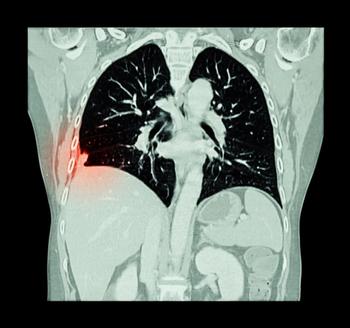
Cost, lower literacy levels and fear of lung cancer diagnosis were highlighted as concerns with lung cancer screening.
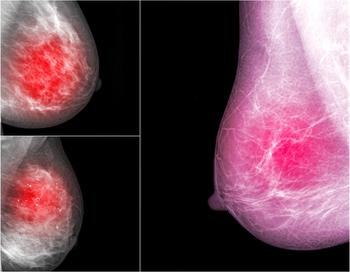
Diffusion-weighted imaging may be useful as a safe and effective screening tool to supplement mammography in women with dense breast tissues.

This study discloses the characteristics of patients using self-scheduled online patient portal screening mammography.
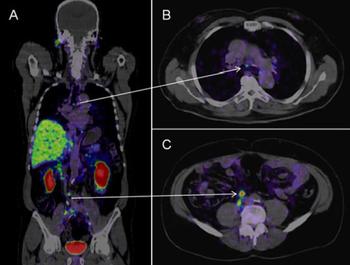
PSMA PET is highly robust in identifying prostate cancer lesions which are otherwise deemed unremarkable.
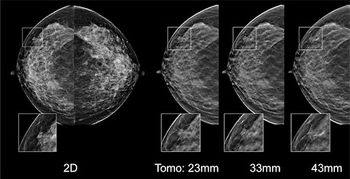
An artificial intelligence for digital breast tomosynthesis enhances radiologists’ performance and efficiency.

Retaining good people should never be about giving them as little as you can get away with for as long as you can.
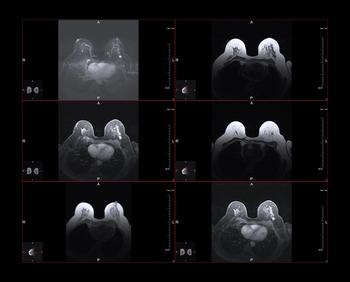
Following breast cancer treatment, women who have access to breast MRI may safely forgo additional mammographic or digital breast tomosynthesis follow-up.
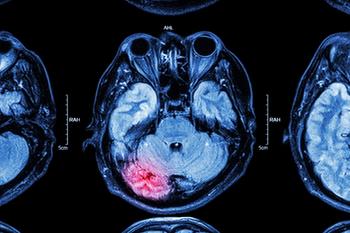
A deep learning model was developed to detect intracranial hemorrhage in computed tomography scans without medical annotation.
Multiparametric MRI can detect pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant therapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.

Sonographic quantitative assessment of the deltoid muscle could translate into a dedicated, simple and noninvasive screening method to detect type 2 diabetes.
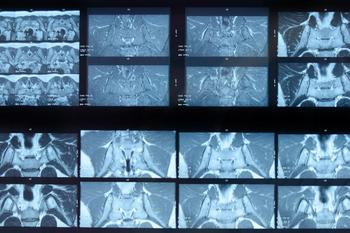
Findings suggest that patients with suspected axial spondyloarthropathy not taking NSAIDs were more likely to have MRI proven inflammation compared with patients taking NSAIDs.
Deep learning models trained on a dataset lacking racial diversity could hinder the detection of pathology in underrepresented minority patients.

Breast ultrasound/MRI fusion significantly improves localization of incidentally detected MRI lesions which are occult on an initial ultrasound survey alone.
COVID-19 can result in cardiac complications including myocarditis, arterial and venous thromboembolism, and cardiomyopathy.

Artificial intelligence has been shown to be beneficial in the discovery of prognostic biomarkers for lung cancer diagnosis, treatment, and response evaluation.

Learn more about what Canon Medical will be showcasing virtually at RSNA 2021.