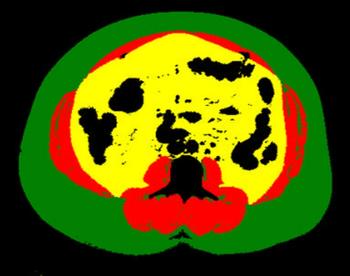
Using deep learning analysis with abdominal CT scans provides a more accurate body composition measurement that can predict which patients will suffer major cardiovascular events within five years.

Using deep learning analysis with abdominal CT scans provides a more accurate body composition measurement that can predict which patients will suffer major cardiovascular events within five years.

Conducting screening mammography on men with a genetic risk for breast cancer can increase early detection, but clinical guidance and recommendations remain inconsistent.

Using high-resolution micro-CT with bones exposed to fire could help forensic investigators determine the timing of murders.
The mechanisms, magnitude, manifestations, and management of stroke during the pandemic.

Bright years are ahead for the industry, according to industry expert Bhavya Rehani, M.D., if focus is given to selfless service, education, technology and innovation, and engaging the global community.

Advanced imaging can help pinpoint the location and cause of lingering nerve damage in patients who have recovered from the virus.
Capturing the scan can reduce number of repeat surgeries and pinpoint additional cancers.

Implementing artificial intelligence tools with breast imaging can pinpoint overlooked interval cancers and decrease provider workload in screening mammography programs.
MRI shows injections can both accelerate healing time and improve range of motion.
What’s critical, and what radiologists can do.

Radiologists have the opportunity to identify women suffering intimate partner violence by detecting a specific type of forearm fracture.

When support staff step in to control communications and keep the workday running smoothly.
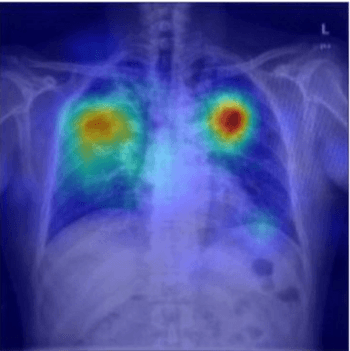
Applying a deep-learning model to a photograph of a chest X-ray can help providers in resource-poor areas diagnose the disease.

A model that uses biomarkers pulled from a woman’s mammogram does produce a more accurate breast cancer risk assessment.
By incorporating non-imaging data, the algorithm can effectively pinpoint which patients will need ICU intervention.

fMRI scans show that babies’ brain activity can be influenced through associative learning, presenting a potential strategy for promoting the development of life-long skills in infants who have injured brains.
Optically pumped magnetometer sensor detects magnetic signals that could augment the detection of traumatic brain injury and disease.
Left atrial diameter and fibrosis differences between African American and white patients could play a role the risk of ischemic stroke.

CT scans reveal impaired lung function in individuals who use biomass, such as wood or wildfires, to cook.
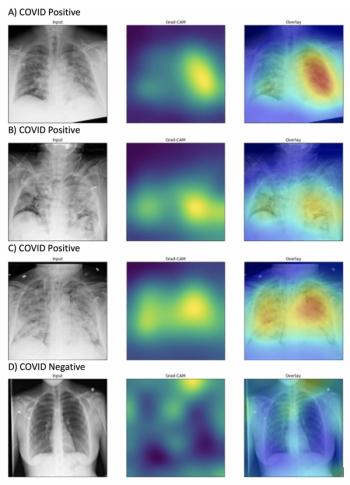
Investigators from Northwestern University have developed an algorithm that can identify evidence of COVID-19 on chest X-rays in a fraction of the time.
Brain MRI scans reveal that anxiety is independently associated with a faster progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease.

Images reveal that adolescents experienced a loss in volumetric bone mineral density after sleeve gastrectomy and extreme weight loss.
An agreement or a promise does not mean much if it is not clear how you can or will reach the goal.

Here's what to expect this week on Diagnostic Imaging.
Swabs created with a 3D printer produce virtually identical diagnostic results, effectively addressing the shortage of nasopharyngeal swabs.
Basic photographs paired with AI technique can pick up on retinal changes that are early signs of the progressive central nervous system disorder.

This mathematical algorithm can reduce dose in pediatric CT scans by 52 percent.

Trends for CT scans for abdominal pain in pediatric patients are down, but they are up for adults. Still, the scan is integrally involved in appendicitis diagnoses.
Third annual report from the American Lung Association reveals 94 percent of high-risk eligible patients are not getting screening with LDCT, and access and outcomes are worse for racial and ethnic minorities.
Rapid COVID-19 Diagnosis with CT and CO-RADS; Cooled Radiofrequency Ablation for Pain Relief; Inappropriate Abdominal CT and Ultrasound Scans; and Lead Shielding Guidance