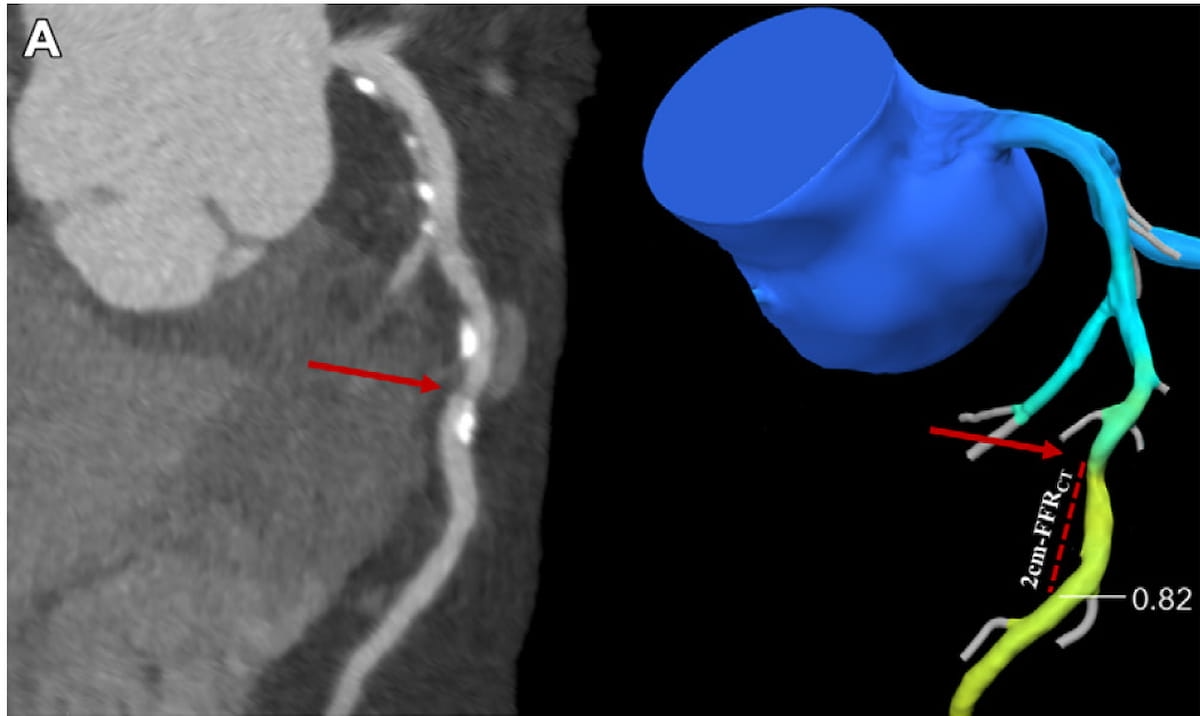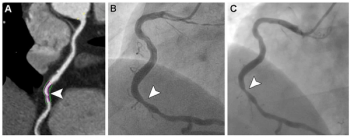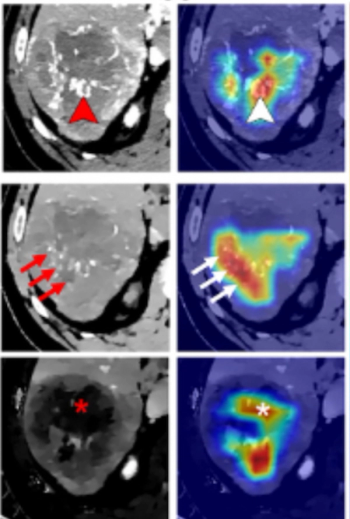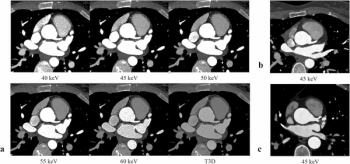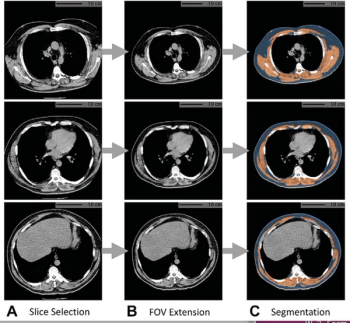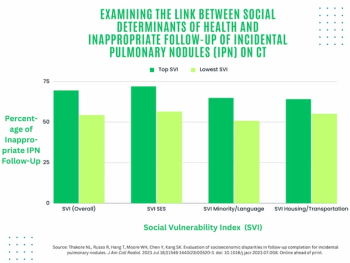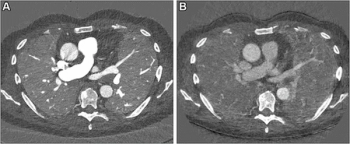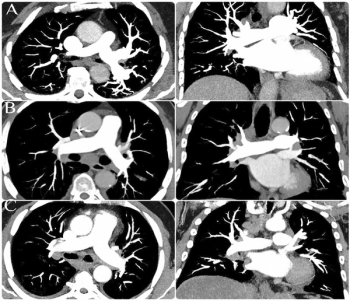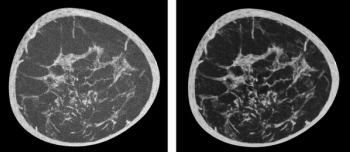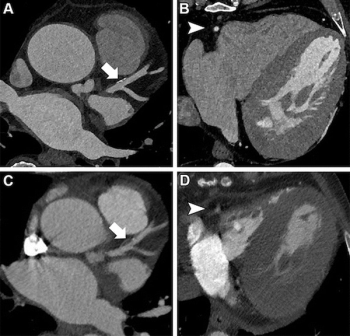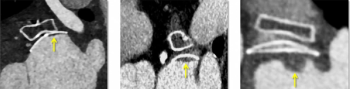
The presence of high-grade hypoattenuation thickening on follow-up computed tomography (CT) after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) procedures for patients with atrial fibrillation was associated with a 4.6-fold risk for stroke, according to newly published research.