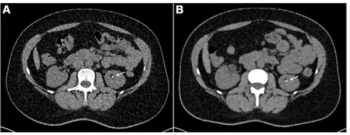
New research shows that photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) at an effective dose of 0.79 mSv provided significantly higher signal-to-noise ratios for urinary calculi (kidney stone) detection than energy-integrating detector CT at 1.39 mSv.

Meta-Analysis: PET/MRI Offers Better Sensitivity for Cardiac Sarcoidosis than PET/CT

CMS Approves NTAP Reimbursement for CT-Based AI Triage Software for Obstructive Hydrocephalus

New research shows that photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) at an effective dose of 0.79 mSv provided significantly higher signal-to-noise ratios for urinary calculi (kidney stone) detection than energy-integrating detector CT at 1.39 mSv.
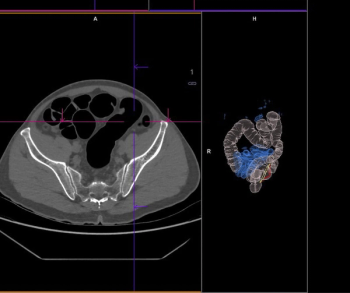
In a 10-year analysis of computed tomography colonography (CTC) use in the United States, researchers found that CTC use increased from 1.4 percent of adults in 2019 to 3.5 percent in 2021.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in July 2024.
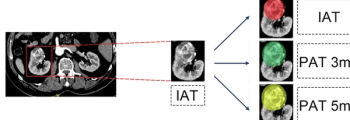
An emerging diagnostic model incorporating radiomic features from intratumoral and peritumoral regions exhibited a 29 percent higher AUC and 77 percent higher sensitivity rate than a clinical model for predicting the grading of clear cell renal cell carcinoma, according to recent research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
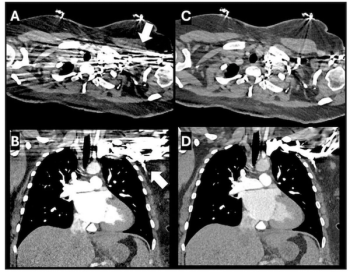
New research looking at photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) demonstrated significantly reduced variation and tracheal air density attenuation with polyenergetic reconstruction in contrast to monoenergetic reconstruction on chest CT.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
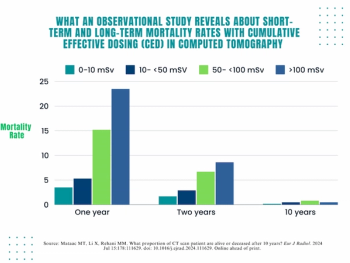
Emerging research suggests CT radiation dosing of 50 mSv or greater is associated with higher mortality at two years but nearly half of those patients were alive 10 years later.
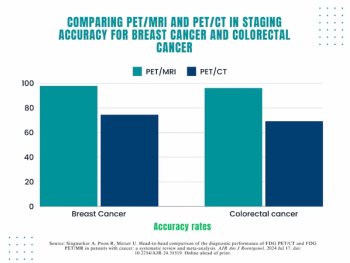
While PET/MRI and PET/CT had comparable sensitivity for patient-level regional nodal metastases and lesion-level recurrence, the authors of a systematic review noted that PET/MRI had significantly higher accuracy in breast cancer and colorectal cancer staging.
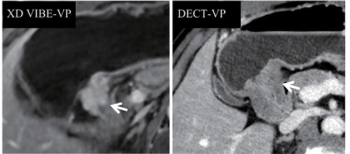
Researchers found that mpMRI was 18 percent more accurate than dual-energy CT (DECT) for T1 staging and 19 percent more accurate for N3 staging of gastric cancer.

Review the case and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
Photon-counting CT-optimized features with the OmniTom Elite system include 30 cm field of view scanning, continuous spiral scanning, and an ultra-high-resolution capability of 0.141 mm resolution.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
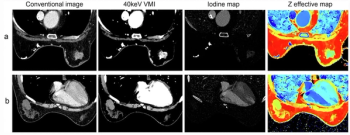
Incorporating age, lesion shape and effective atomic number in the venous phase of dual-energy CT (DECT), an emerging model demonstrated a 79.1 percent AUC for differentiating between malignant and benign breast lesions.
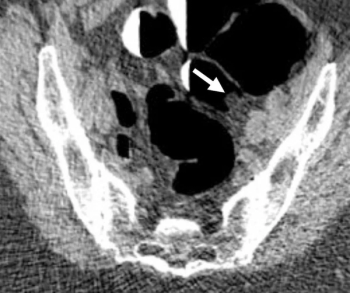
In newly issued proposals addressing changes to coverage for Medicare services in 2025, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) announced its intent to provide coverage of computed tomography colonography (CTC) for Medicare beneficiaries in 2025.
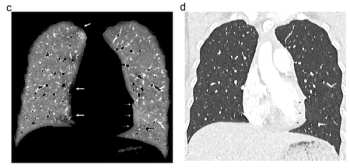
Photon-counting CT enables enhanced fissure visualization and a lower degree of cardiac motion artifacts for lung perfusion imaging at a significantly reduced scan time in contrast to dual-energy CT, according to new research findings.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in June 2024.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Proprietary technologies with the FCT iStream computed tomography system reportedly facilitate enhanced workflow efficiency and significantly reduced radiation dosing.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
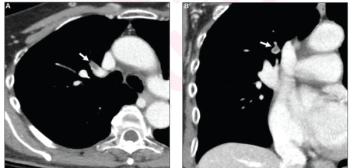
Artificial intelligence facilitated a 96.2 percent sensitivity rate for incidental pulmonary embolism (IPE) on contrast-enhanced CT chest or abdomen exams, according to new prospective research involving over 4,300 patients.
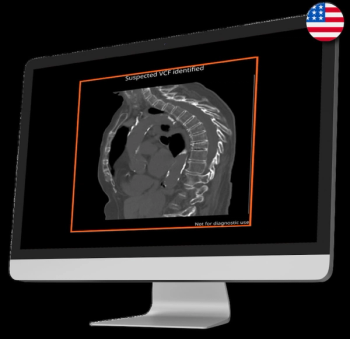
The AI-enabled CINA-VCF algorithm can reportedly detect vertebral compression fractures within seconds after assessment of chest or abdominal CT scans.
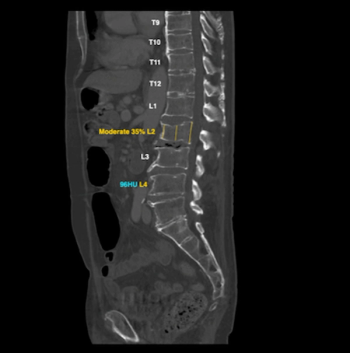
Facilitating additional consultation on chest and abdominal CT scans, the Second Opinions teleradiology platform now features FDA-cleared AI tools for cardiac, bone and liver assessments.
An AI algorithm that incorporates scoring of coronary inflammation based on coronary CT angiography (CCTA) may enhance long-term cardiovascular risk stratification beyond conventional risk factor and imaging assessments, even in patients without obstructive CAD.