
Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
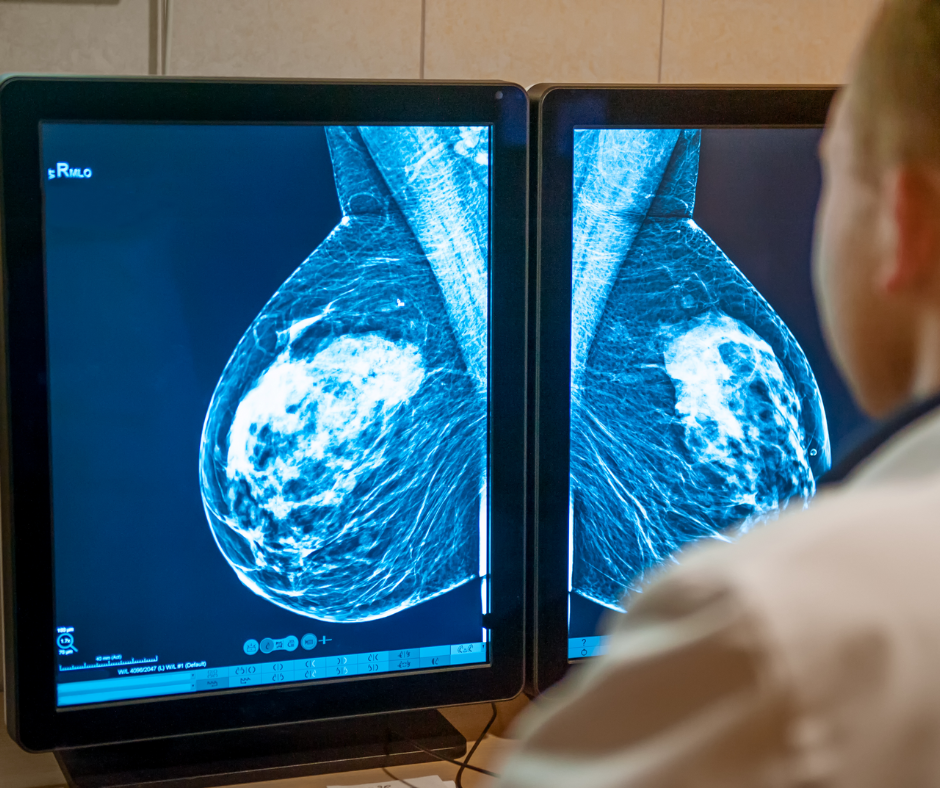
New research from the American Cancer Society comparing pre-pandemic cancer screening prevalence to the second year of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States showed a 1.1 million decrease in breast cancer screenings, a 4.4 million decrease in cervical cancer screening and a 600,000 decrease in prostate cancer screenings.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

The upgraded, artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled software for the Swoop® Portable MR Imaging System reportedly enhances the device’s signal-to-noise ratio for diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequences.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
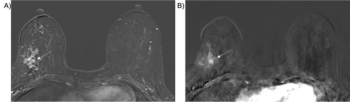
In a new study that may have implications for breast cancer surgery, researchers found that shorter time to enhancement (TTE) on preoperative ultrafast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was significantly associated with escalation of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) to invasive breast cancer.
In a new study of 1,232 women diagnosed with breast cancer within a year of a screening mammography exam, researchers found that interval breast cancer was 17 percent more likely in women with dense or extremely dense breasts, and over three times more likely to involve stage 2 or higher primary tumors in comparison to screening-detected breast cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
While acknowledging a moderate to high risk of bias in the retrospective studies reviewed for a recent meta-analysis, researchers found the current evidence supports the use of high-intensity magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) surveillance for detection of soft tissue sarcoma recurrence.

In a study of over 9,000 children that examined structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data as well as parent and child self-reporting of adversity-related measures, researchers found that greater exposure to adversities for Black children was linked to lower gray matter volume in the amygdala and multiple subregions of the prefrontal cortex in comparison to White children.
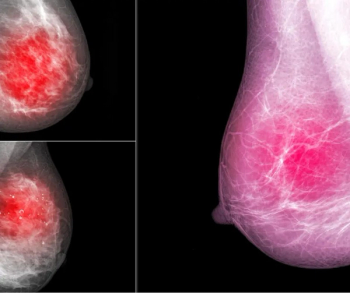
In a review of 22 studies and data from over 132,000 women with dense breasts and negative mammography exams, researchers found that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was superior to digital breast tomosynthesis, handheld ultrasound and automated whole breast ultrasound for the detection of breast cancer.
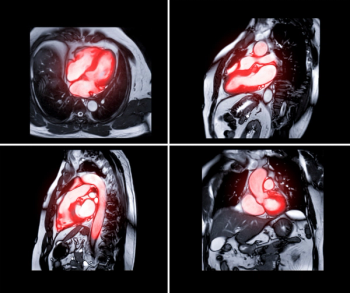
In a prospective study of over 600 patients, researchers found that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) had no serious adverse effects upon the detection of tachyarrhythmias with non-MRI conditional implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
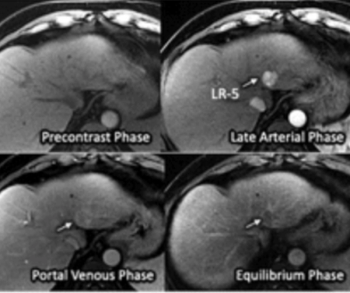
In a multicenter study involving nearly 300 patients, researchers found that abbreviated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) had a sensitivity rate of 88.2 percent and a specificity rate of 89.1 percent for detecting early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).

For system errors and failures in radiology, are we prone to a satisfaction of search that prevents us from addressing deeper issues?

Check out the top radiology content of the past week.
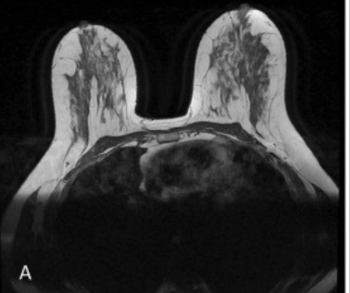
Emerging research suggests that magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may help downgrade nearly 10 percent of suspected BI-RADS 3 lesions from ultrasound imaging
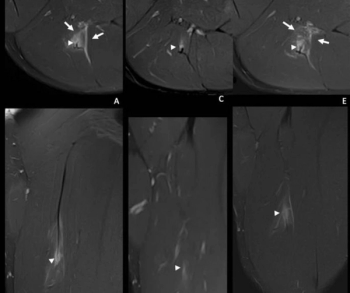
In a study looking at acute muscle injuries in professional athletes, the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) within a week prior to their return to play demonstrated significant re-injury risk with intermuscular edema, callus gap and transversal and/or mixed connective tissue gap.

Catch up on the most well-read magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) articles from 2022.
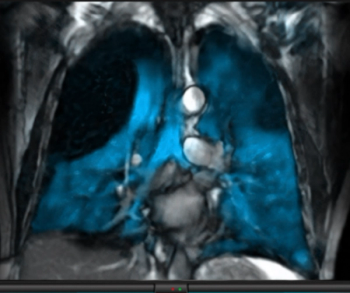
An inhaled contrast agent used with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Xenoview™ (xenon Xe 129 hyperpolarized) reportedly provides regional mapping of lung ventilation without patient exposure to ionizing radiation.

Catch up on the most well-read artificial intelligence (AI) articles from 2022.

Catch up on the most well-read Image IQ quizzes from 2022.

Catch up on the most well-viewed video interviews from Diagnostic Imaging in 2022.

Touching on a variety of topics in radiology, here are the top five most well-read articles from Diagnostic Imaging in 2022.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research of the past month.

Check out the top radiology content of the past week.
In addition to summary sensitivity and specificity of 92 percent and 91 percent respectively for characterization of indeterminate adnexal lesions, the meta-analysis on pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed higher summary malignancy rates for O-RADS MRI 4 and 5 lesions than predicted.