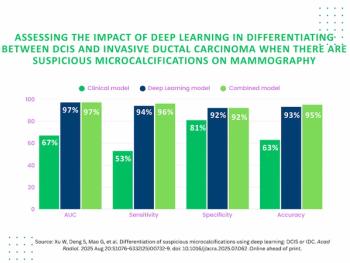
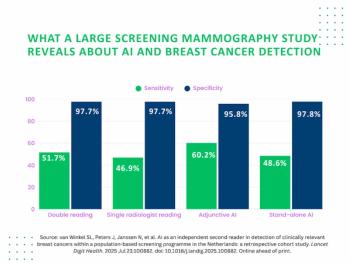
In a recent interview, Zeeshan Shah, M.D., discussed the challenges of addressing rising breast imaging volume amid the radiologist shortage, the potential of emerging AI solutions for bolstering efficient triage and an increasing incidence of breast cancer presentations in younger patients.