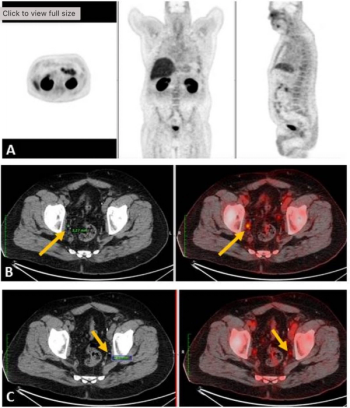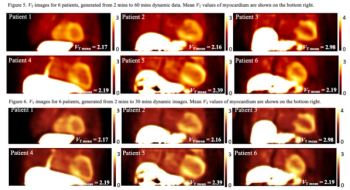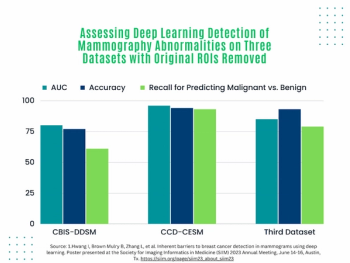
In a video interview, Hong Song, M.D., Ph.D., discussed retrospective research, presented at the recent Society for Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) conference, that evaluated the combination of artificial intelligence (AI)-based software and the PSMA agent piflufolastat F 18 to help quantify prostate cancer lesions and associations with biochemical progression-free survival.