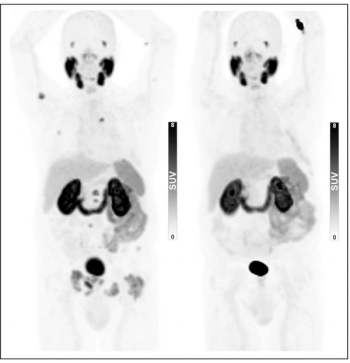
For patients 80 years of age or older that have a PSA level at 20 ng/mL or higher, PSMA PET/CT has a high likelihood of success in diagnosing and staging prostate cancer regardless of pre-imaging biopsy use, according to newly published research.

For patients 80 years of age or older that have a PSA level at 20 ng/mL or higher, PSMA PET/CT has a high likelihood of success in diagnosing and staging prostate cancer regardless of pre-imaging biopsy use, according to newly published research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
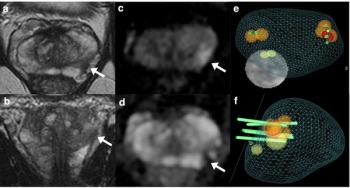
The use of non-contrast, biparametric MRI (bpMRI) for prostate cancer screening regardless of PSA values detected more clinically significant cases of prostate cancer than reserving bpMRI for patients with elevated PSA levels, according to preliminary findings from an ongoing prospective, randomized study.
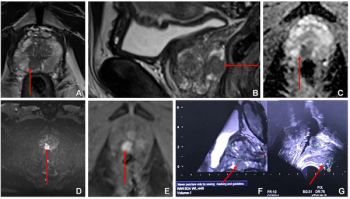
In a study of 413 men with suspected prostate cancer, researchers found the combination of ultrasound and multiparametric MRI-targeted biopsy with systematic biopsy diagnosed prostate cancer in 72.9 percent of patients in comparison to 60.2 percent with systematic biopsy alone.

Catch up on the top radiology news of the past week.
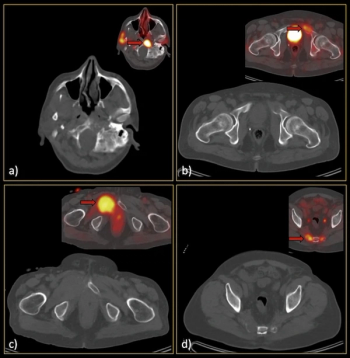
In a study of 601 patients with prostate cancer, researchers found that only one patient with extensive metastasis was falsely diagnosed as non-metastatic on whole-body, low-dose computed tomography (CT) by reviewing radiologists.
A newly published review of 29 prospective studies revealed the use of MRI-guided daily adaptive SBRT in the management of prostate cancer was associated with significantly lower risks of acute grade 2 or higher genitourinary (GU) and gastrointestinal (GI) toxicities in comparison to CT-guided non-adaptive SBRT.

Examining the use of the Response Evaluation Criteria in Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) PET/CT (RECIP 1.0) model for assessing the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, researchers found robust agreement between quantitative application of RECIP via tumor segmentation software and qualitative application of the model through reads by nuclear medicine physicians.
Patients with extraprostatic extension (EPE) on pre-prostatectomy MRI had a 3.6-fold higher risk for biochemical recurrence (BCR) of prostate cancer and a 25 percent lower three-year BCR-free survival rate in comparison to patients without EPE on pre-op MRI, according to newly published research.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

The prospective multicenter trial, which is slated to begin patient recruitment in late 2023, will reportedly assess the ability of 64Cu SAR-bisPSMA to diagnose prostate cancer within pelvic lymph nodes.

Carch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

The approval of Blue Earth Diagnostics' Posluma (flotufolastat F 18) is a significant step forward for PSMA PET imaging, but will it actually help improve patient outcomes?
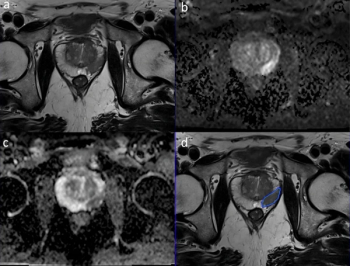
In multiple datasets from a study involving reviewed data from over 2,700 bi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, a deep neural network demonstrated area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) scores ranging from 87 to 89 percent for the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
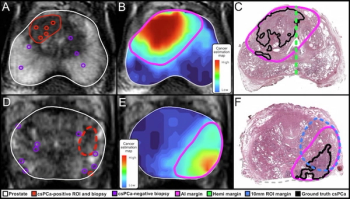
Combining multimodal imaging data and biopsy data, an artificial intelligence (AI) model provided enhanced sensitivity for defining prostate cancer tumor margins in comparison to conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) assessments.

For patients initially diagnosed with non-metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer, pelvic lymph node involvement and five or more polymetastases detected with prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)/ positron emission tomography (PET) are significantly associated with lower overall survival rates, according to recently presented research at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) conference.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
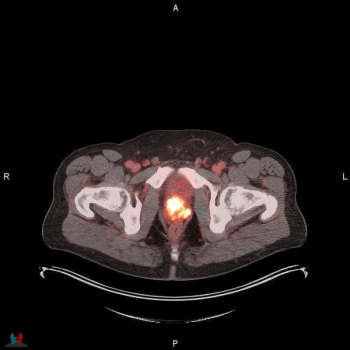
Reportedly the first FDA-approved PSMA PET agent with proprietary radiohybrid technology, POSLUMA can be utilized for positron emission tomography (PET) scans of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) positive lesions in men with prostate cancer and suspected metastasis, and those with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on an elevated serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research from the past month.
In a multinational, multicenter study of over 1,000 patients with recurrent prostate cancer, researchers developed and validated a nomogram that achieved a 72 percent concordance index for the prediction of biochemical recurrence after PSMA PET-guided salvage radiotherapy.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
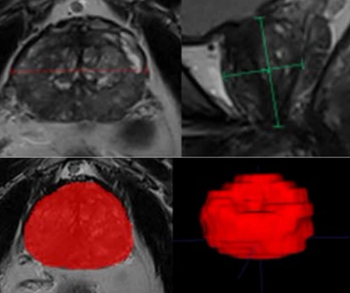
The use of adjunctive artificial intelligence (AI) reportedly improved lesion level sensitivity by nearly 19 percent and patient level specificity by 14 percent for the diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

In a recent video interview from the American Urological Association (AUA) 2023 Annual Meeting, Brian Helfand, M.D., discussed emerging research that shows the potential viability of the agent F18-rhPSMA-7.3 for enhancing the detection of prostate cancer recurrence and facilitating earlier intervention for patients with low prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels.