Ultrasound Detects as Much Pediatric IBD as MR Enterography
MRE may overestimate the presence of disease when using a scoring system.
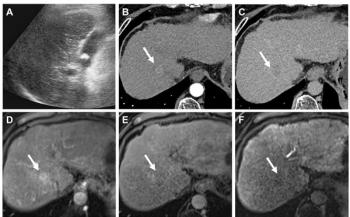
Ultrasound (US) detects as much clinically significant bowel disease as does magnetic resonance enterography (MRE), the current gold standard for imaging, according to a study published in the journal
Researchers from the United Kingdom performed a retrospective cohort study of children and adolescents to determine whether US is as good as MRE for the detecting inflamed bowel, using a combined consensus score as the reference standard.
Fifty-three children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who underwent MRE and US within 4 weeks of the study start were assessed. MRE was scored using the London score and US with a score adapted from the METRIC (MR Enterography or Ultrasound in Crohn’s Disease) trial. Four gastroenterologists assessed an independent clinical consensus score. A combined consensus score using the imaging and clinical scores was agreed upon and used as the reference standard to compare MRE with US.
The results showed that at a whole-patient level, MRE scores were 2 percent higher than US scores, using Lin coefficient to assess inter-observer variability. The repeatability of MRE scores was poor (Lin 0.6). Agreement for US scoring was substantial (Lin 0.95). There was a significant positive correlation between MRE and clinical consensus scores and US and clinical consensus scores.
The researchers concluded that US detected as much clinically significant bowel disease as MRE. They also noted that it was possible that MRE overestimated the presence of disease when using a scoring system. “This study demonstrates the feasibility of using a clinical consensus reference standard in pediatric IBD imaging studies,” they wrote.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.