Intestinal ischemia diagnosed with contrast-enhanced ultrasound
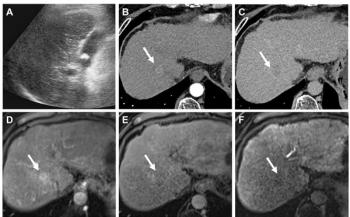
Researchers in Japan have found contrast-enhanced ultrasound with advanced dynamic flow is a highly sensitive way of showing intestinal ischemia in patients with bowel obstruction and very useful for diagnosing the condition. They found diminished and absent color signals during ultrasound exams indicated the presence of intestinal ischemia.
Researchers in Japan have found contrast-enhanced ultrasound with advanced dynamic flow is a highly sensitive way of showing intestinal ischemia in patients with bowel obstruction and very useful for diagnosing the condition. They found diminished and absent color signals during ultrasound exams indicated the presence of intestinal ischemia.
Dr. Toshihide Hamada and colleagues in the gastroenterology department at Miyoshi Central Hospital in Hiroshima, Japan, published their research in the Aug. 6 issue of the British Journal of Radiology. They examined 50 patients admitted for bowel obstruction.
Ultimately, surgery established that nine patients had bowel strangulation, four had superior mesenteric artery thromboembolism, and four had nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia, totaling 17 patients with intestinal ischemia.
Prior to surgery, all 50 patients were administered galactose-based contrast agent SHU 508A. Ultrasound exams focused on the least peristaltic and/or the most dilated segments of the intestines. There the researchers classified color signals from the bowel wall as normal, diminished, or absent. Exams were later correlated with surgical findings.
Color signals were absent in six of the patients with bowel strangulation, all four of the patients with superior mesenteric artery thromboembolism, and two with nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia. Signals were classified as diminished in two more of the patients with bowel strangulation and the other two with mesenteric ischemia. Exams looked normal in 33 patients with simple obstruction and one of the patients with bowel strangulation. This means the test has a sensitivity of 94.1%, a specificity of 100%, a positive predictive value of 100%, and a negative predictive value 97.1%.
The researchers acknowledged this was only their preliminary experience, but they consider contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with advanced dynamic flow to be a highly sensitive method for diagnosing intestinal ischemia in patients with bowel obstruction.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.