Carotid ultrasound predicts stroke, heart attack risks
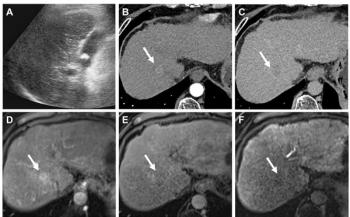
Carotid artery plaque examinations performed with serial ultrasound scans could help identify patients at high risk for a heart attack or other potentially lethal cardiovascular conditions.
Dr. Markus Reiter, at the Medical University of Vienna, evaluated 1268 asymptomatic patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease using computer-assisted gray-scale median (GSM) ultrasound carotid measurements. Plaque volume identified carotid disease in 574 patients who had a second ultrasound exam six to nine months later to measure plaque changes. Nearly half of those patients had lower GSM levels, and 37% experienced a major adverse cardiovascular event, such as a heart attack, a stroke, or cardiac surgery, within three years of the second ultrasound. Vulnerable carotid plaque indicated not only increased risk of stroke but also disease progression elsewhere in the cardiovascular system.
Study results appeared in the September issue of Radiology.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.