Women's Health CT
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

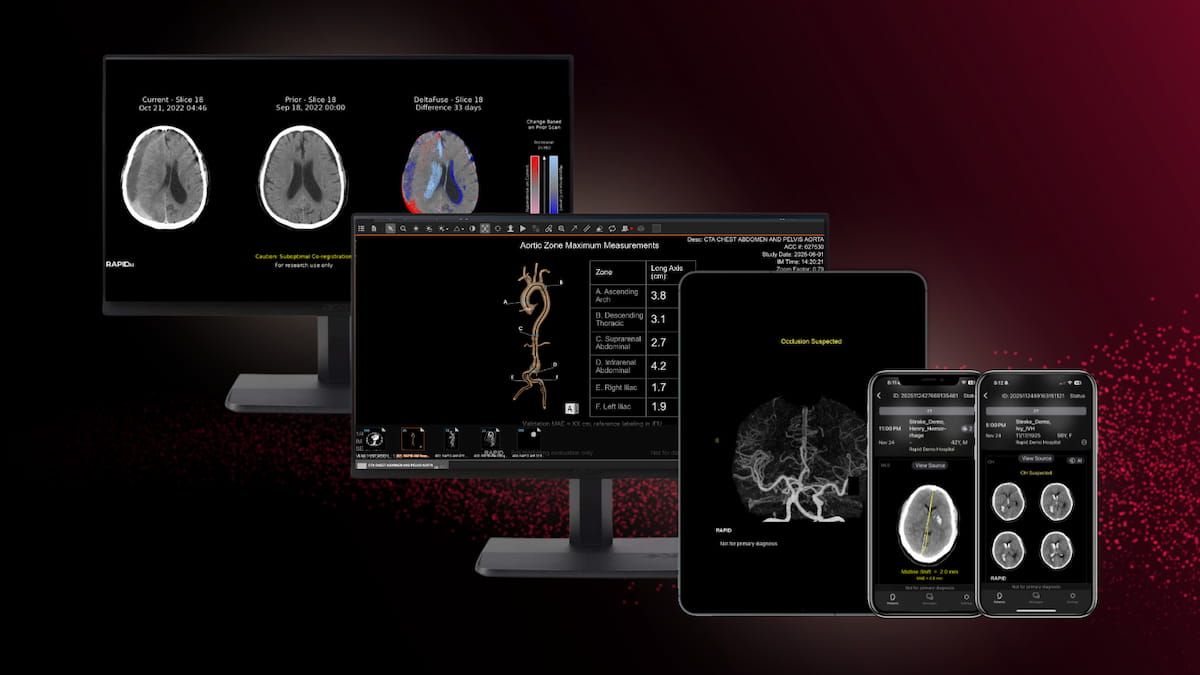
Along with the capability of automated measurements and 3D reconstructions of the aorta, Rapid Aortic may facilitate earlier detection of aortic aneurysms and dissections on computed tomography exams.
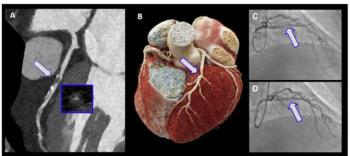
Photon-counting computed tomography demonstrated over 20 percent accuracy at the patient level and nearly 14 percent higher accuracy level at the vessel level in comparison to energy-integrating detector CT for detecting > 70 percent stenosis, according to a newly published study.
The launch of the AVI imaging platform reportedly facilitates direct integration into PACS and RS systems, and automated access to adjunctive CT-based AI applications for a variety of conditions including pulmonary embolism, intracranial hemorrhage and large vessel occlusion
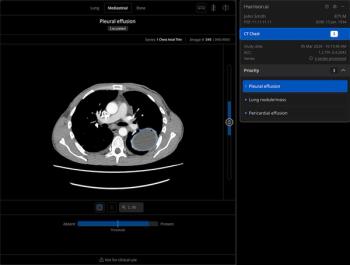
Offering a “safety net” in emergency and inpatient settings, the Chest CT software reportedly provides enhanced triage capabilities and adjunctive detection of 167 radiological features.

In a recent interview, Timothy Fairbairn, Ph.D., and Fatima Rodiguez, M.D., discussed new research findings, recently presented at the American Heart Association (AHA) conference, showing the value of AI-powered quantification of plaque burden from CCTA exams for predicting adverse cardiovascular outcomes.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
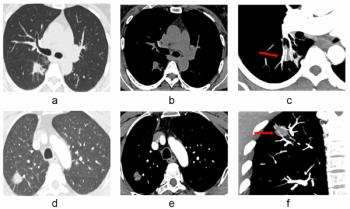
New research shows that incorporating the CT vascular sign into assessments of pulmonary nodules led to significant increases in specificity and accuracy as well as reduced false positive rates for differentiating between malignant and benign solid pulmonary nodules.
The Harrison.ai Open Platform reportedly emphasizes open architecture, customer ROI and elimination of costly AI platform fees.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
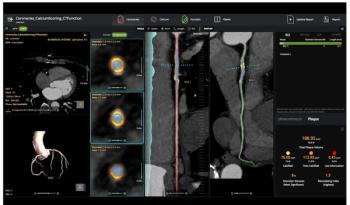
The AI-powered cvi42 | Plaque software enables adjunctive on-site interpretation of coronary CT angiography (CCTA) scans for plaque quantification.
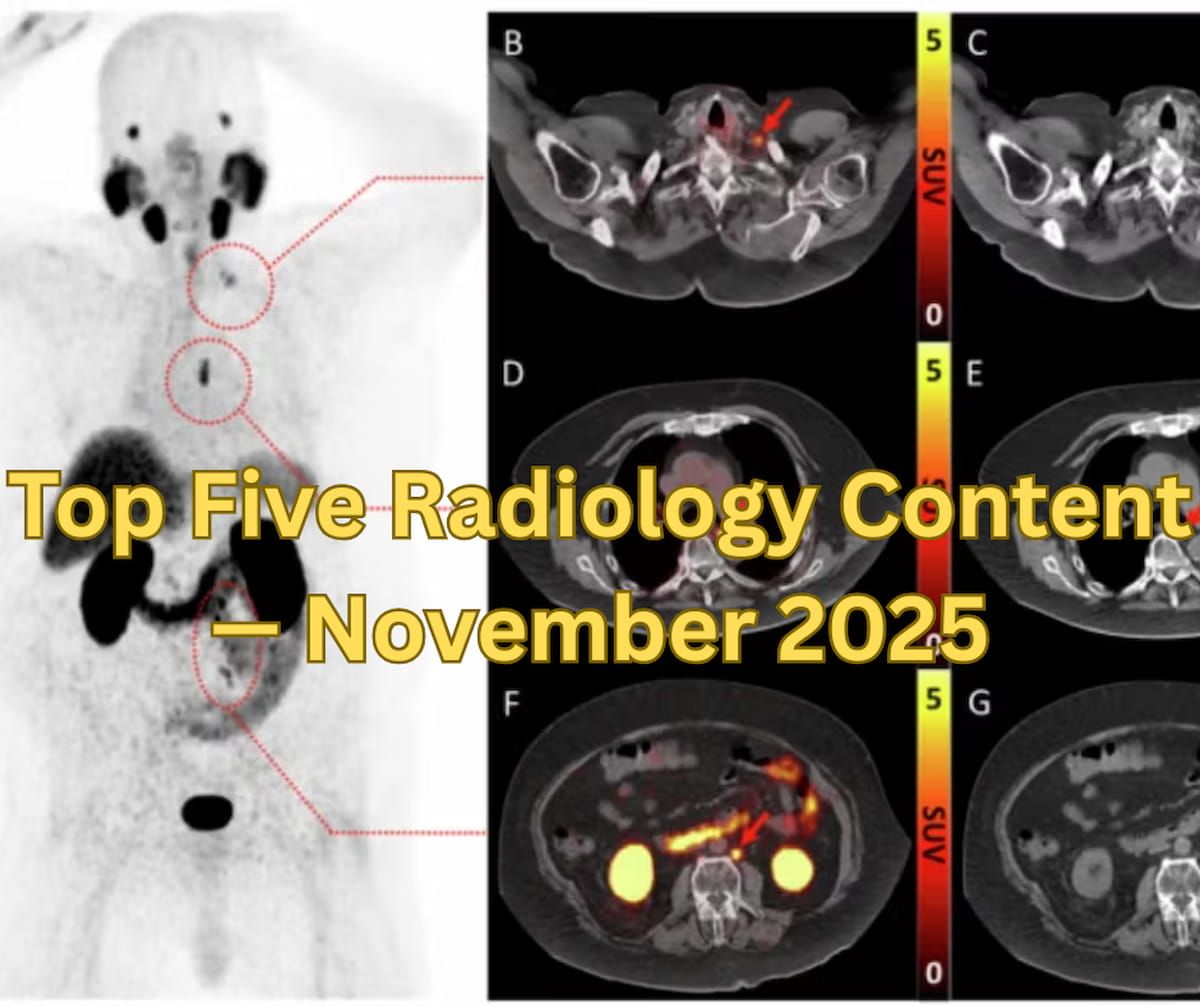
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in October 2025.
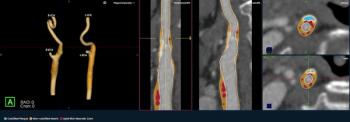
The newly launched PlaqueIQ™ image analysis modality is reportedly the first CT-based software indicated for the quantification and classification of plaque morphology in the carotid arteries.
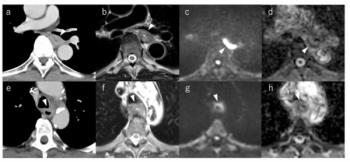
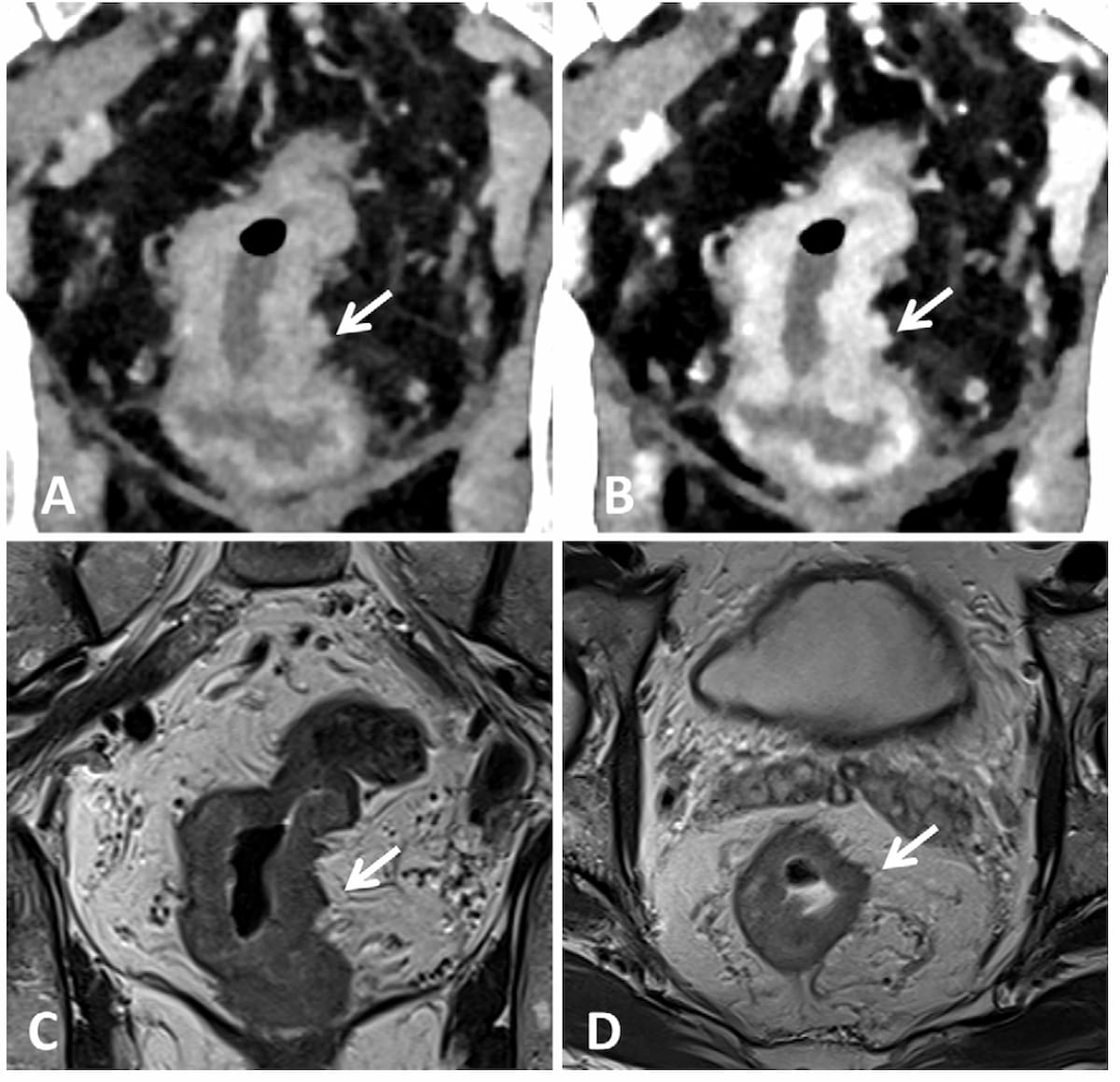
For patients with esophageal cancer, preoperative MRI demonstrated an average AUC above 94 percent for detecting tracheal invasion in contrast to an AUC range between 52.9 and 70.6 percent for CT, according to a recently published study.

The AI-enabled e-Lung software may lead to significantly improved and earlier detection of progressive pulmonary fibrosis, even in patients deemed clinically stable, according to new research recently presented at the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) conference.
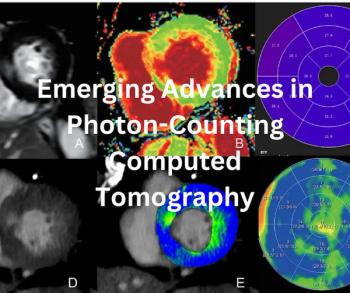
New research on photon-counting computed tomography in 2025 reveals increasing capabilities of the technology to enhance CT visualization and characterization with significant reductions in radiation dosing in cardiovascular imaging, abdominal imaging and other diagnostic applications.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
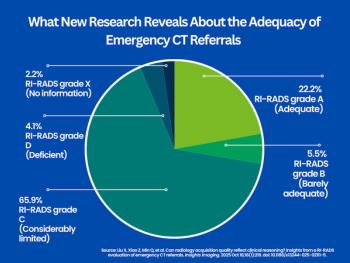
In a review of nearly 1,300 emergency referrals for computed tomography (CT) scans, approximately 28 percent were deemed to have adequate requisition quality according to a RI-RADS analysis.
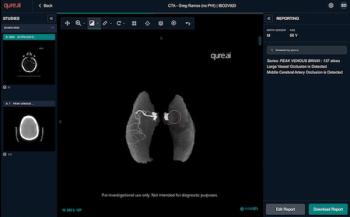
Facilitating timely triage, the qER-CTA software enables AI assessment of the internal carotid artery and M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery for possible large vessel occlusions (LVOs).

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

The AI-enabled LungQ® 4 software reportedly offers enhanced segmentation of peripheral airways and estimates of chronic perfusion deficits based on analysis of chest CT scans.
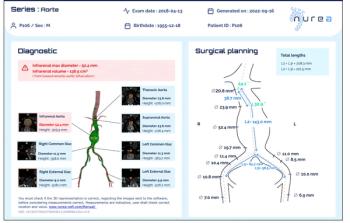
Facilitating timely detection and follow-up management of patients with aortic aneurysms, the PRAEVAorta2 software reportedly enables automated measurement of aortic diameters on computed tomography (CT) scans.
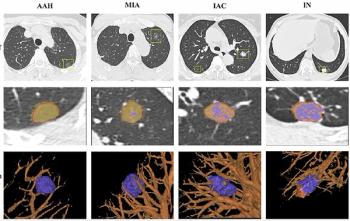
A deep learning AI platform, which incorporated radiomic features including CT attenuation metrics, demonstrated a 93.6 percent AUC for detecting invasive adenocarcinoma on chest CT.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
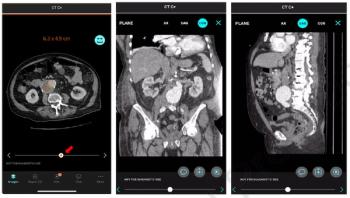
In a study involving over 500 patients, researchers noted that the CT-based AI software led to a 24 percent increase of evaluations for aortic abdominal aneurysms within six months of detection.