Designed for full-body imaging, the new modality reportedly offers a lightweight portable design, AI-powered tools and enhanced high-resolution images.
In a recent interview, Atul Gupta, M.D. discussed the evolution and potential impact of Fiber Optic RealShape (FORS) technology, which uses light instead of radiation to facilitate real-time 3D imaging that may lead to significant efficiencies with complex aortic procedures.

Designed for full-body imaging, the new modality reportedly offers a lightweight portable design, AI-powered tools and enhanced high-resolution images.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in February 2024.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
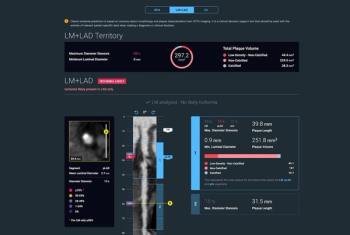
Clinicians can bill Category 1 CPT Code 75580 for adjunctive use of the artificial intelligence (AI)-powered Cleerly Ischemia software for fractional flow reserve estimates based on coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) scans.
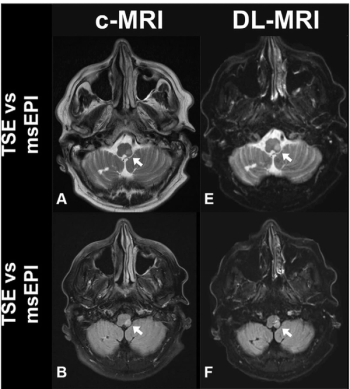
For patients with suspected acute stroke, researchers noted higher image quality for deep learning-accelerated MRI, which can be completed over 11 minutes sooner than similar sequences for conventional MRI.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
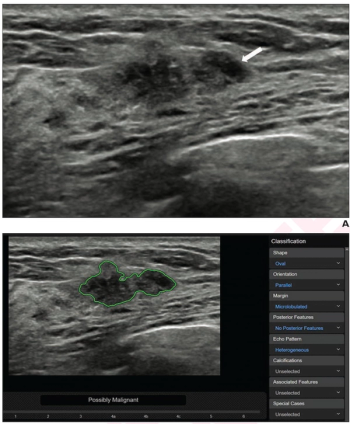
What does the current evidence reveal for four FDA-cleared AI software modalities for breast ultrasound? Leading researchers review the study findings in a recently published literature review.
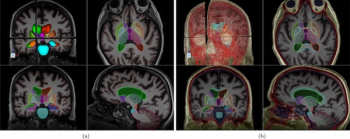
Offering rapid automated segmentation of brain structures, the ClearPoint 2.2 software reportedly enhances visualization for a variety of targeted, MRI-guided procedures.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
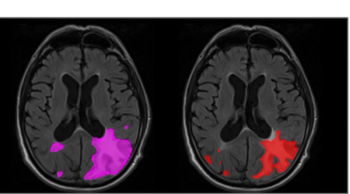
The adjunctive use of AI software led to 16 percent and 10 percent increases in sensitivity rates for the detection of ARIA-E and ARIA-H, respectively, in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, according to newly published research.
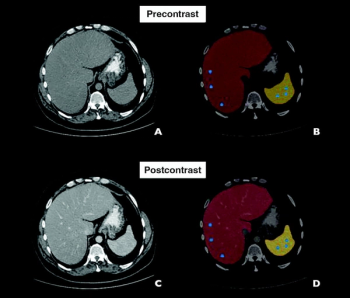
The AI-enabled HealthFLD software demonstrated a 77.8 percent sensitivity rate and a 93.2 percent specificity rate for diagnosing moderate hepatic steatosis on contrast-enhanced CT scans in a recent study of over 2,900 patients.
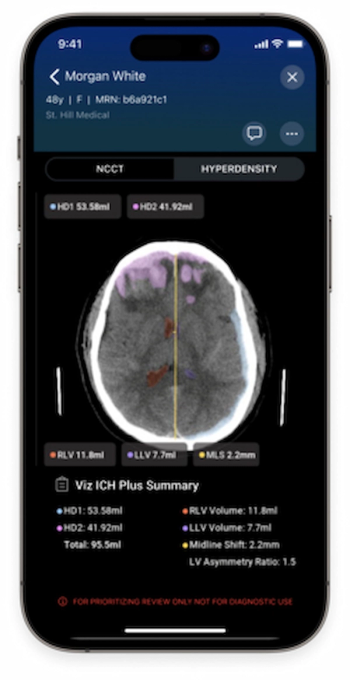
Facilitating timely diagnosis and intervention for brain bleeds, the artificial intelligence (AI)-powered Viz ICH Plus software may provide quantified assessment for intracranial hyperdensities, lateral ventricles and midline shifts.
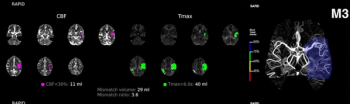
The use of multiple artificial intelligence (AI) modalities to assess blood vessel density reduction and computed tomography perfusion (CTP) mismatch values facilitated a 93.3 percent detection rate for medium vessel occlusions, according to research presented recently at the International Stroke Conference.
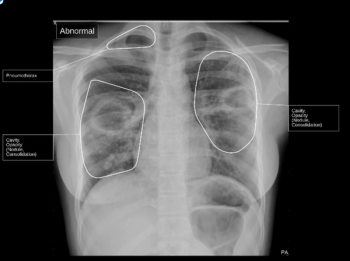
With reported increases in tuberculosis cases after the COVID-19 pandemic, the qSpot-TB adjunctive artificial intelligence (AI) device may facilitate improved diagnosis of the disease on chest X-rays.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
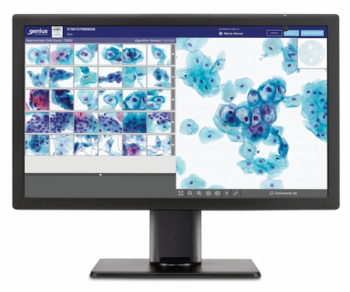
Combining advanced volumetric imaging technology with deep learning, the Genius Digital Diagnostics System has reportedly shown a 28 percent reduction in false negatives for high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and other severe lesions in comparison to microscopic review.
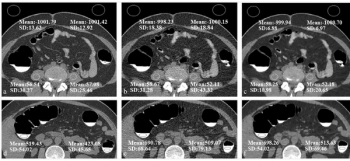
Researchers found the use of deep learning reconstruction for computed tomography colonography (CTC) led to 25 percent higher subjective image quality scoring than iterative image reconstruction at a substantially reduced rate of radiation dosing.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in January 2024.
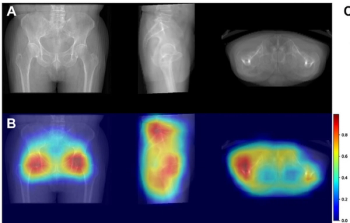
Employing reconstructed radiographs from 3D hip CT scans, a deep learning model demonstrated a higher concordance index (C index) and higher two- and three-year AUCs than multiple imaging models and three clinical models for predicting subsequent fracture risk in patients with hip fractures.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

The new Category I CPT code reportedly facilitates a nearly 7 percent increase in reimbursement for use of the CT-based fractional flow reserve assessment of coronary blood flow.
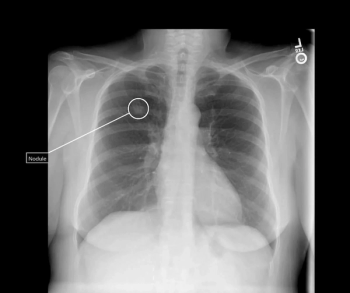
In a recently issued statement from multiple radiology societies including the RSNA and ACR, researchers offer practical advice for evaluating artificial intelligence (AI) tools, implementing AI into current workflows and monitoring of the technology to help ensure optimal benefit and effectiveness.
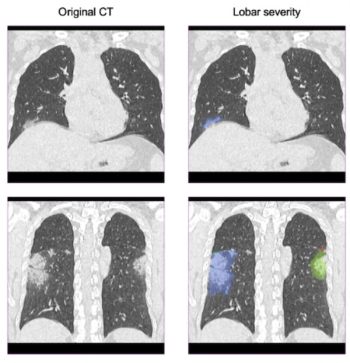
Reportedly offering improved delineation of pulmonary structures and greater accuracy with computed tomography (CT) values of pulmonary tissue, the artificial intelligence (AI)-powered LungQ 3.0.0. may facilitate enhanced precision and efficiency with interventional procedures such as lung volume reduction and ablation procedures.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.