
Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
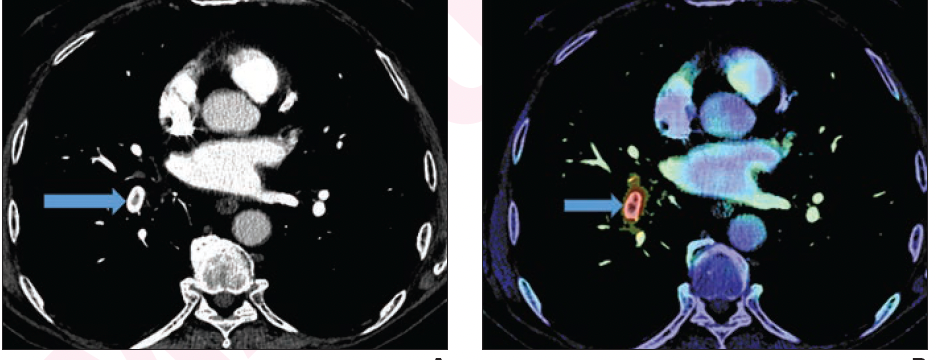
A recent study showed that artificial intelligence (AI)-based worklist reprioritization led to a mean reduction of 12.3 minutes in radiology report turnaround time for positive computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) exams that were positive for pulmonary embolism.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
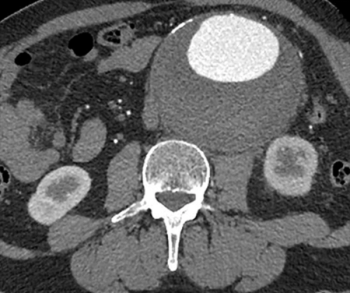
Viz AAA is reportedly the first artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled algorithm to garner FDA 510(k) clearance for the detection of abdominal aortic aneurysm.
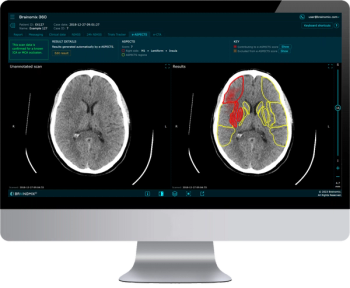
Through artificial intelligence (AI) assessment of non-contrast computed tomography (CT) scans, the Brainomix 360 e-ASPECTS software provides an automated ASPECTS score and heatmap to enhance stroke imaging.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
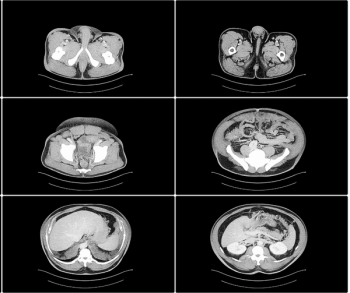
Noting that computed tomography (CT) scans are obtained for more than 30 million emergency department (ED) patients annually and that 31.3 percent of ED CT scans reveal incidental findings, representatives from the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) recently collaborated on best practice recommendations for addressing incidental imaging findings in EDs.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
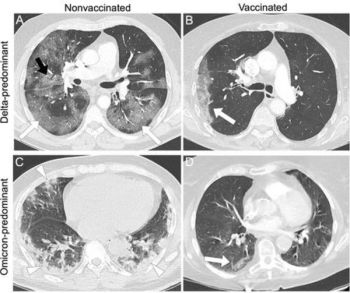
Emerging research from a multicenter study found that COVID-19 vaccination was affiliated with a lower likelihood of high computed tomography (CT) severity scores and typical CT findings for COVID-19 in comparison to unvaccinated patients.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
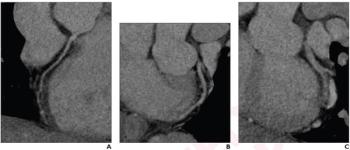
Recently published research revealed that coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) exams performed with dual-source CT were completed 22 minutes faster and had a nearly 28 percent higher frequency of good or excellent image quality in comparison to CCTA exams performed with single-source CT devices.
The new launches include the 80/160-slice computed tomography (CT) scanner Aquilion Serve, which allows simultaneous previews of axial, lateral and AP views, and Celex, a multipurpose X-ray system that offers automated and customizable features to help maximize workflow efficiencies.
New research from the American Cancer Society comparing pre-pandemic cancer screening prevalence to the second year of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States showed a 1.1 million decrease in breast cancer screenings, a 4.4 million decrease in cervical cancer screening and a 600,000 decrease in prostate cancer screenings.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
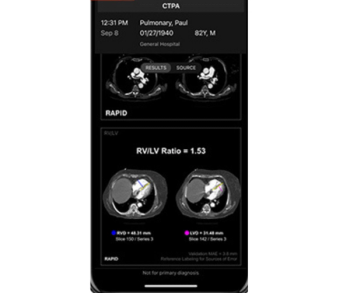
Facilitating expedited assessment of pulmonary embolism severity, the emerging artificial intelligence (AI) tool Rapid RV/LV reportedly calculates the right ventricle/left ventricle (RV/LV) ratio within minutes of a computed tomography pulmonary angiogram (CTPA).
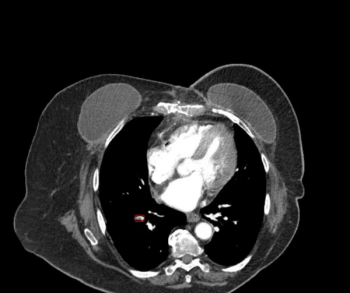
Noting that only 25 percent of incidental emboli are identified in reporting of initial computed tomography (CT) exams, Avicenna.AI said the artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled CINA-iPE is geared toward detecting incidental pulmonary embolism (PE) on chest CT scans.
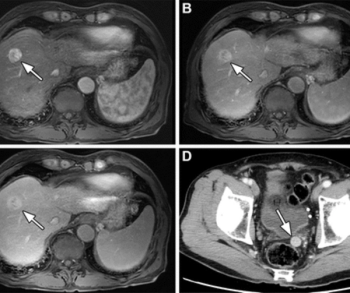
Noting that pelvic coverage can increase radiation dosing for liver computed tomography (CT) by 29 to 39 percent, researchers found low three-year cumulative rates of incidental pelvic tumors and isolated pelvic metastasis in follow-up liver CT imaging of over 1,100 people treated for hepatocellular carcinoma.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
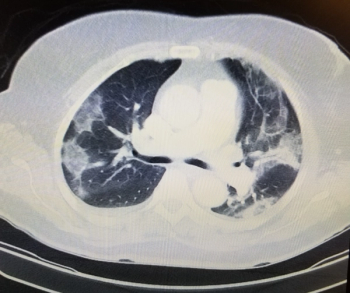
The computed tomography severity score (CTSS) has sensitivity rates of 85 percent for predicting the severity of COVID-19 and 77 percent for predicting COVID-19 related mortality, according to a newly published meta-analysis.
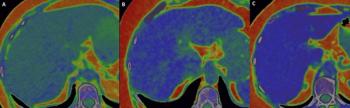
Preliminary research suggests no significant differences between photon-counting computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the quantification of liver fat fraction in obese patients.
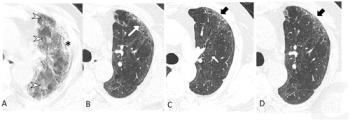
In their review of follow-up chest computed tomography (CT) scans, researchers from Wuhan, China found that nearly 40 percent of patients had interstitial lung abnormalities two years after having COVID-19.
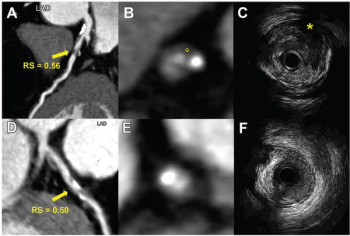
Derived from coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) images, a radiomics model demonstrated a 75 percent or greater area under the curve (AUC) in multiple test sets for identifying vulnerable plaque.