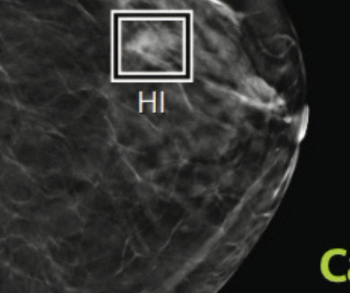
The artificial intelligence (AI) software Saige-Density™ reportedly provides automated assessment of breast density during mammography exams.

The artificial intelligence (AI) software Saige-Density™ reportedly provides automated assessment of breast density during mammography exams.
Reportedly the first targeted molecular imaging agent to provide intraoperative illumination of lung cancer, Cytalux (pafolacianine) helped identify clinically significant events in more than 50 percent of patients undergoing surgery for confirmed or suspected pulmonary nodules, according to Phase 3 trial data presented earlier this year at the American Association for Thoracic Surgery Annual Meeting.

Having interests outside of one’s chosen profession provides more of a multifaceted perspective and potentially more door-opening opportunities in the future.

Check out the top radiology content of the past week.
In addition to summary sensitivity and specificity of 92 percent and 91 percent respectively for characterization of indeterminate adnexal lesions, the meta-analysis on pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed higher summary malignancy rates for O-RADS MRI 4 and 5 lesions than predicted.
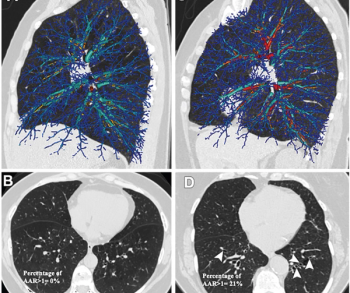
Employing an artificial intelligence (AI) tool to quantify airway-to-artery (AAR) diameter ratios on chest computed tomography (CT), researchers found the percentage of airways with an AAR greater than 1 was associated with increased pulmonary exacerbations in ever-smokers.

In an interview at the recent Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, Alex Pozdnyakov, M.D. discussed findings from a new meta-analysis, which revealed that prostate-specific membrane antigen/positron emission tomography (PSMA PET) imaging in patients with prostate cancer recurrence led to treatment changes that resulted in a pooled 60.2 percent rate of prostate cancer-free survival at 20 months.
In a recent interview at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, Eliot Siegel, M.D., discussed a variety of potential benefits with cloud-based image management in radiology, ranging from enhanced data security and economies of scale to improved access to a variety of artificial intelligence (AI) solutions to increase efficiency.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
In a study of nearly 18,000 men who had prostate cancer screening, researchers found the use of pre-biopsy magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for those with elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels and reserving MRI-targeted biopsy for those with PI-RADS scores of 3 to 5 reduced the risk of detecting clinically insignificant cancers by half.

Relief from looming reimbursement cuts, a PACS system that allows customized keyboard shortcuts and consistently relevant clinical histories are a few of the items on the wish list for this radiologist.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

In a recent video interview from the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, Tessa Cook, MD, PhD discussed new research on automated de-identification in radiology reports and the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) to help address time-consuming challenges in the radiology workflow.
In a new study based on five- to six-year follow-up data from over 650,000 children and young adults who had at least one computed tomography (CT) exam prior to the age of 22, researchers found a “strong dose-response relationship” between increased CT radiation exposure and brain cancer.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
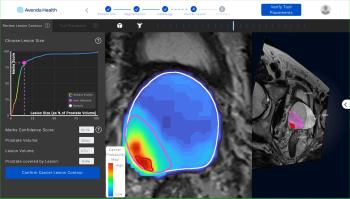
The Food and Drug Administration has granted 510(k) clearance to iQuest (Avenda Health), an artificial intelligence (AI) platform that combines findings from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), pathology reports and biopsy results to facilitate three-dimensional mapping of prostate cancer.

The EchoGo® Heart Failure device reportedly has an 87.8 percent sensitivity rate and an 83 percent specificity rate for diagnosing heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, an increasingly prevalent but frequently misdiagnosed condition.
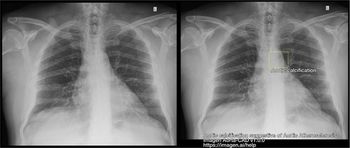
One study showed use of the Aorta-CAD cloud-based software led to a 62 percent reduction of missed aortic calcification that suggested aortic atherosclerosis.
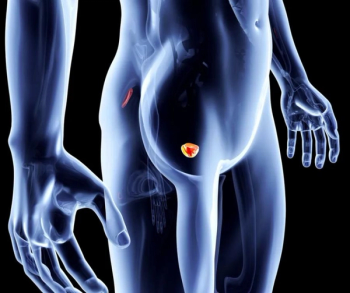
For patients recently diagnosed with prostate cancer, the emerging positron emission tomography (PET) agent 18F-rhPSMA-7.3 reportedly has a 96 percent specificity rate for detecting pelvic lymph node metastases, according to Phase 3 study results recently presented at the 22nd Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO).
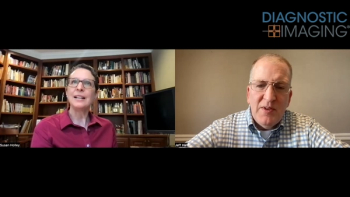
In a recent video interview, Susan Holley, MD discussed key findings from a large retrospective longitudinal study, presented at the recent Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, which found that an emerging artificial intelligence (AI) model was over 24 percent more consistent than radiologist assessment of breast density.
Lamenting the deteriorating quality of clinical histories that radiologists receive from referring clinicians, this author comically speculates about clinical histories one may see in the near future.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
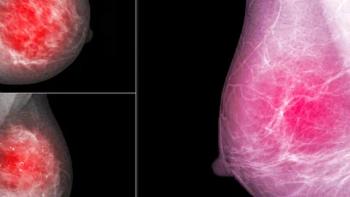
In a recent lecture at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, Wendy DeMartini, MD, discussed a variety of preliminary proposed changes to the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) for breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examinations.
In what may be the first study to assess the effectiveness of biparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for prostate cancer screening in a large cohort, researchers found that MRI screening had a significantly lower false positive rate and significantly higher positive predictive values (PPVs) than prostate-specific antigen (PSA)-based screening.

In a recent video interview, Raymond Y. Kwong, MD, discussed his clinical experience with the Vista.ai (formerly HeartVista) One Click MRI software and recent research, presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, that revealed a 31 percent decrease in cardiac MRI scan times for patients with cardiomyopathy or structural heart disease.
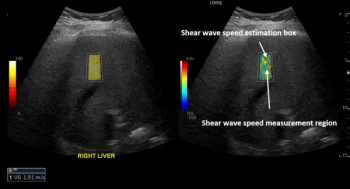
The retrospective study involving the use of ultrasound shear wave elastography showed a significant increase in liver stiffness 44 weeks after the diagnosis of COVID-19 in comparison to pre-pandemic and pandemic controls.
Main pulmonary artery and right ventricular diameters on computed tomography (CT) scans of the thorax were predictors of pulmonary hypertension.
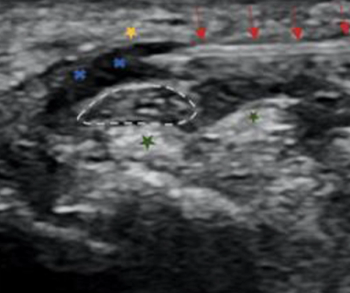
A randomized controlled trial shows that the minimally invasive treatment provided long-term relief of carpal tunnel syndrome.
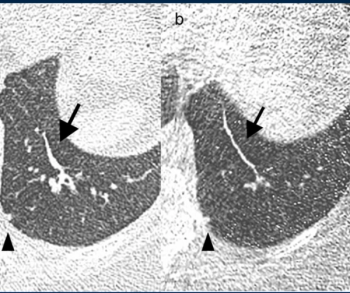
Ultra-low-dose computed tomography (ULDCT) may have similar efficacy as low-dose CT (LDCT) for detecting a variety of pulmonary conditions in people with current or past smoking histories, but had poor detection of ground glass opacification lesions, according to a recent prospective study presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

Recently launched at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference, the SIGNA Experience reportedly features synergistic technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) advances that help improve the efficiency and quality of magnetic resonance imaging.