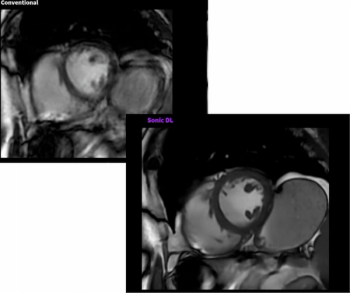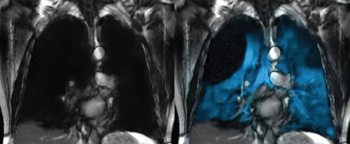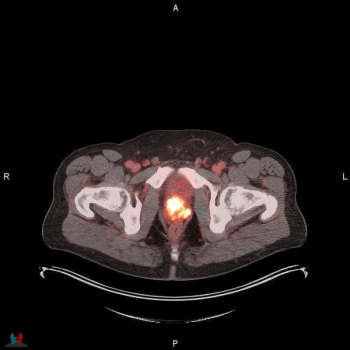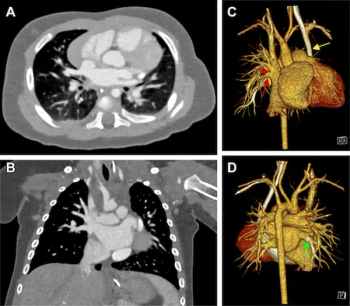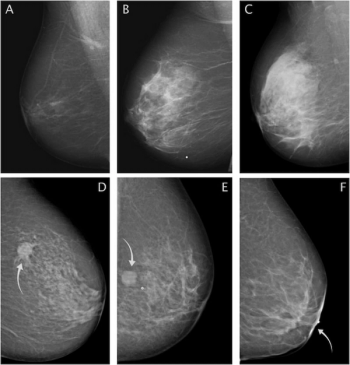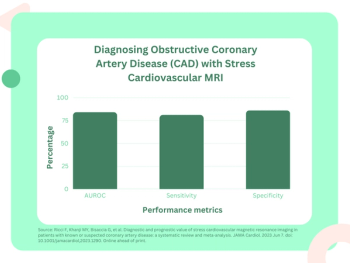
For the detection of obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD), stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrated a sensitivity rate of 81 percent and a specificity rate of 86 percent, according to a meta-analysis of 64 studies and data from 74,470 patients with stable chest pain.