
Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In a newly published meta-analysis of 24 studies, researchers noted that the PSMA PET radiotracer 18F PSMA-1007 may provide more benefit than 68Ga Ga-PSMA-11 for primary staging of patients with prostate cancer and detection of local lesion recurrence, but also has drawbacks with higher liver uptake and multiple reports of false positive bone lesions.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
Offering an all-in-one platform of artificial intelligence (AI) applications, MyBreastAI Suite reportedly facilitates early breast cancer detection and enhances efficiency with breast imaging workflows.
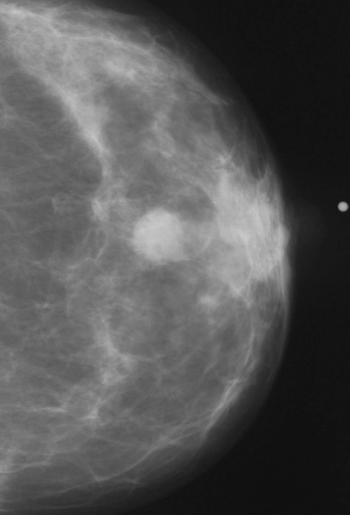
Consistent adherence to the five most recent mammography screenings prior to a breast cancer diagnosis reduced breast cancer death risk by 72 percent in comparison to women who did not have the mammography screening, according to new research findings presented at the annual Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.

In a recent interview at the annual RSNA conference in Chicago, Richard Heller, MD discussed the impact of reduced reimbursement rates in radiology, the projected CMS conversion factor for 2024, the severity of payment cuts in interventional radiology and the importance of radiologist advocacy.
BrainSpec Core reportedly offers enhanced sensitivity for low-grade gliomas and may facilitate the diagnosis of conditions including Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and epilepsy.

Dr. Kottler sat down with Diagnostic Imaging at RSNA 2023 to discuss AI imaging milestones and the potential impact of AI on workflows in radiology.

People who smoke marijuana and cigarettes have 12 times the risk for centrilobular emphysema than non-smokers, according to new computed tomography (CT) research presented at the annual Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference.
Excess verbiage, at the behest of non-clinical interlopers, continues to pervade radiology reports.
The Aquilion ONE/Insight Edition and Aquilion Serve SP computed tomography (CT) systems reportedly offer enhanced deep learning reconstruction and intuitive workflow efficiencies.
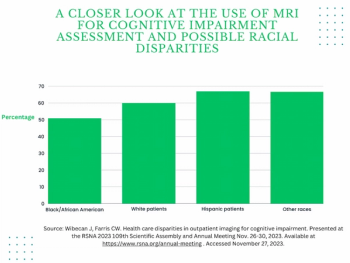
In a four-year study of over 1,600 patients who had outpatient head CTs, head CT angiography and/or brain MRI to assess cognitive impairment, researchers found that Black patients were over 9 percent less likely than White patients and over 16 percent less likely than Hispanic patients to receive brain MRI.
In a recent interview about President Biden’s recent executive order on artificial intelligence (AI), Morris Panner, the president of Intelerad Medical Systems, shared his concerns that the executive order, while well-intentioned, may wind up stifling innovation and the continued evolution of AI in radiology.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.

With algorithms utilized in aerospace technology, the CT LVAS software reportedly provides enhanced assessment of regional airflow and lung ventilation.
The Biograph Vision.X positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) reportedly offers an industry-leading time of flight (TOF) and detector technology that facilitates the diagnosis of smaller lesions.
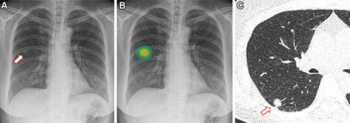
Artificial intelligence (AI) assessments of chest X-rays identified 28 percent of a 17,000 plus cohort of never-smokers as being at high-risk for lung cancer, according to research to be presented at the annual Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference next week.
Pixyl.Neuro reportedly leverages generative artificial intelligence (AI) technology to accelerate brain MRI assessment and improve early detection of abnormal atrophy.

Review the case study and test your knowledge to make the correct diagnosis.
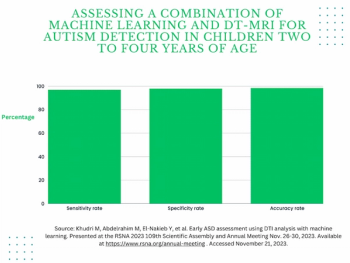
Through assessment of diffusion tensor MRI of the brain, a new AI system reportedly offers a 97 percent sensitivity rate in diagnosing autism in children between two to four years of age, according to research to be presented at the annual Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference next week.
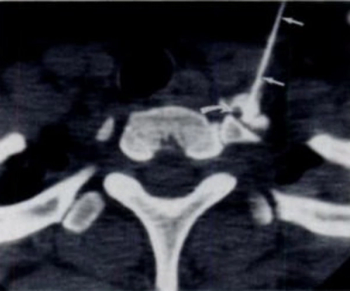
Utilizing computed tomography (CT) guidance, researchers have found that performing a minimally invasive anesthetic injection into the stellate ganglia may help address parosmia due to COVID-19, according to study results that will be presented at the annual Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) conference next week.

The artificial intelligence (AI)-powered technology reportedly offers decreased noise magnitude while enhancing image reconstruction for cardiovascular computed tomography (CT) scanners.
Can a return to a per-click reimbursement model reignite one’s drive?

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
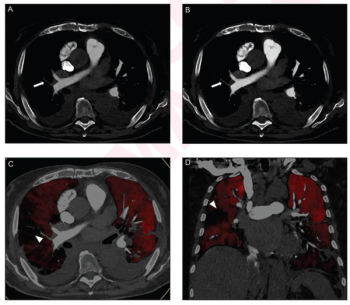
Performing computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) with a high-pitch photon counting detector (PCD) offers enhanced signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) at a reduced radiation dose in comparison to employing an energy-integrating detector (EID), according to new research.
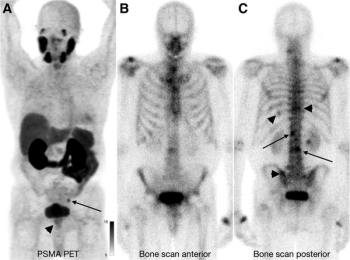
Fifty-seven percent of patients with prostate cancer diagnosed with osseous metastases on bone scans had negative findings on PSMA PET imaging, according to findings from an international multicenter comparative study.
Offering a combination of simplified and personalized scanning for patients at significantly lower lifecycle costs than other dual-source CT systems, the Somatom Pro.Pulse may be a viable option for smaller rural facilities and outpatient imaging centers.
Combining enhanced imaging capabilities, workflow efficiencies and artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled technology to improve the diagnosis and management of health conditions in women, Samsung has launched the V6 ultrasound system.
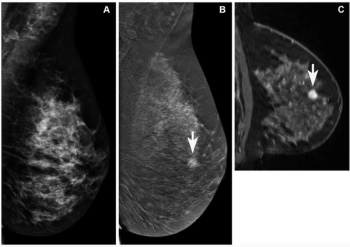
In findings from an enriched cohort of asymptomatic patients with screening-detected abnormalities, researchers found that contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) was superior to conventional mammography and offered equivalent detection of breast cancer in comparison to breast MRI and abbreviated breast MRI.
Providing automated brain volume calculations based on MRI images, NeuroShield’s artificial intelligence (AI)-powered technology may help facilitate treatment for neurodegenerative conditions ranging from Alzheimer’s disease to epilepsy.