Report from AIUM: 4D ultrasound bolsters diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis
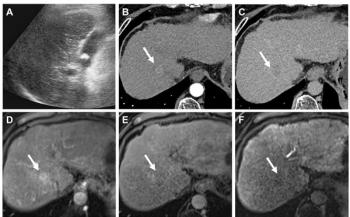
Three-dimensional Doppler ultrasound can provide a quick, reliable diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis with just one sweep in real-time, according to a study presented Monday at the 2005 American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine meeting.
Three-dimensional Doppler ultrasound can provide a quick, reliable diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis with just one sweep in real-time, according to a study presented Monday at the 2005 American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine meeting.
Standard scanning with 2D color Doppler enables physicians to gauge blood velocity and flow by combining vessel measurements at different points. Using 4D Doppler with the Encore PV system (VueSonix Sensors), physicians can assess the peak systolic velocity and volume flow of the common, internal, and external carotid arteries within a single volume in 10 seconds almost automatically, said principal investigator Flemming Forsberg, Ph.D.
Forsberg, a professor of radiology at Thomas Jefferson University, and colleagues assessed 117 sets of vessels in 59 patients with suspected carotid artery stenosis. The investigators compared The Encore PV measurements with those of a conventional ultrasound system. They found that the semiautomated 4D Doppler device measurements were as reliable as those of 2D.
The researchers obtained two volumes of the internal carotid to determine the reproducibility of the test. They compared the Encore PV and 2D ultrasound data using linear regression, kappa statistics, and Bland-Altman analysis.
Four-D peak systolic velocity and volume flow measurements of the internal carotid artery were reproducible. Bland-Altman analysis of 2D versus 4D showed acceptable variation for the peak systolic velocity in the common, internal, and external carotid arteries.
Measurements of peak systolic velocity with 2D and 4D correlated in all three vessels, and the correlation was statistically significant (p
The semiautomated volume measurements may help eliminate time-consuming factors associated with 2D and could make volume-flow and other calculations more user-friendly. Physicians might be able to identify patients with severe stenosis using not only velocity and flow measurements, but physiological parameters as well, Forsberg said.
Newsletter
Stay at the forefront of radiology with the Diagnostic Imaging newsletter, delivering the latest news, clinical insights, and imaging advancements for today’s radiologists.